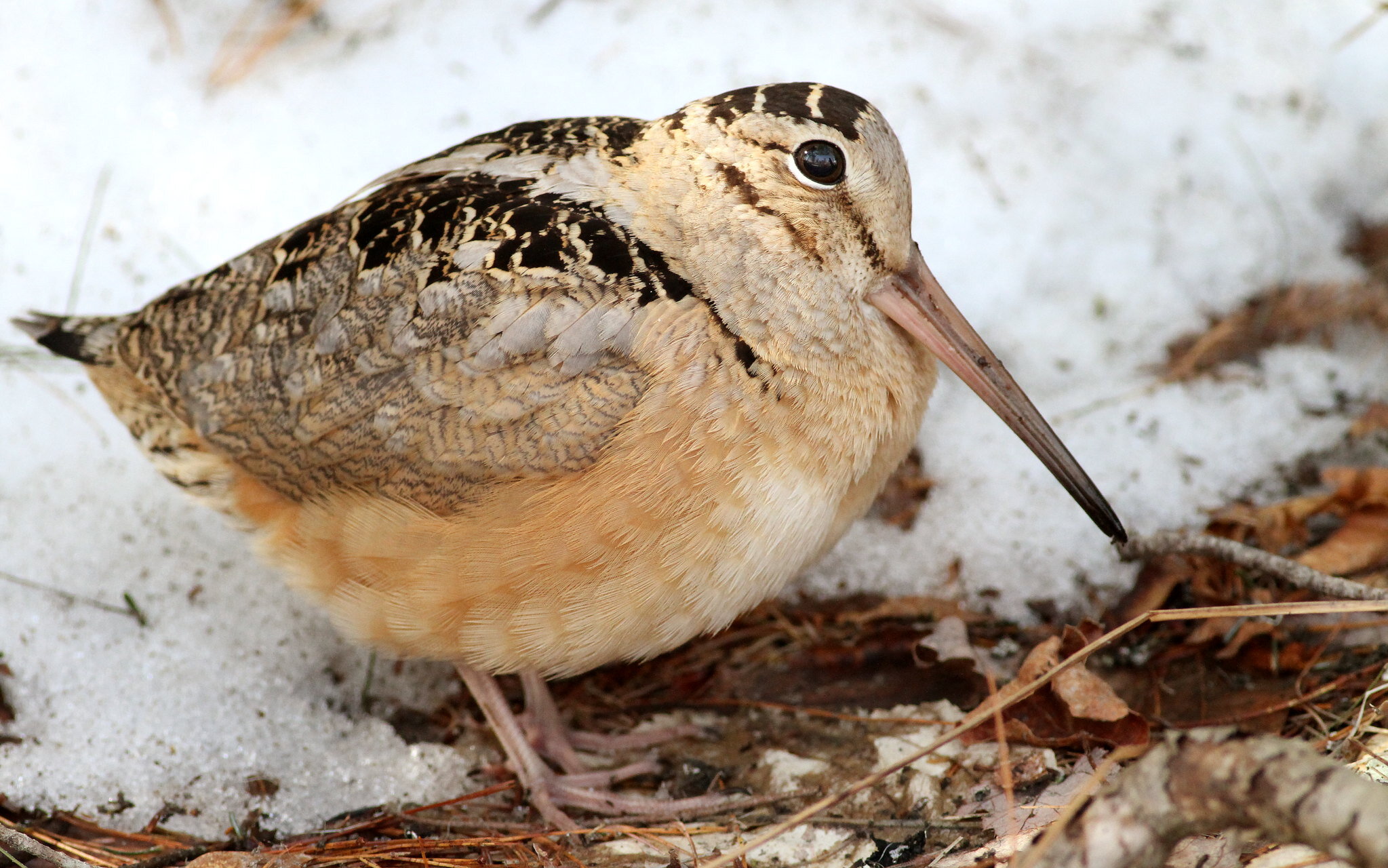
Virginia rails seem to walk on water. Photo by Arlene Koziol
“Secretive marsh birds” sounds like a church festival band or a clandestine middle school group. However, in nature, secretive marsh birds include rails and bitterns, where they dwell in wetland realms rarely breached by humans. Though the birds are not objectively secretive, they are indeed hard to spot from where humans stand.
Virginia rails provide a terrific look into the adaptations of marsh birds; the vocalizations alone seem like they could come from any number of species. Its “k-k-k-kerrrrrr” trill sounds like the note of a spring peeper. Its “kiddick” call sounds like a malfunctioning dial-up internet connection. Its grunts are low, fuzzy, and accentuated by squeaks.
This rail builds up to 30 dummy nests in a year, resembling the crazed paranoia of another marshland counterpart, the marsh wren.
If you have walked in a marsh where a Virginia rail has walked, you might be aware how maladapted humans are to these environments and you might gain respect for the Virginia rail. On floating mats at the edge of open water, we punch through; whereas Virginia rails stay upright with their light bodies and wide feet, probing on mudflats and floating mats of marsh. Where species like rice cutgrass, sedges, leatherleaf, stunted shrubs, and poison sumac might cause unholy irritation in humans, the Virginia rail’s laterally compressed body and tough forehead feathers allow it to scurry through wetland vegetation with ease. Anyone who has walked through a southern Wisconsin marsh has come to realize that rubber boots quickly become overtopped and the pure muscle and flexibility needed to high-step through a marsh builds up plenty of lactic acid. Here too, rails outclass us, with the highest ratio of leg muscles to flight muscles in birds, explaining their tenacity in marshes and their reluctant and haphazard flight.
Check out the giant feet on this Virginia rail chick! Photo by Mick Thompson
Research has shown that Virginia rails can be quite discerning in terms of their habitat preferences. On average, wetlands dominated by the invasive reed canary grass make poor habitat for rails. With predators of their eggs like mink, otter, great horned owls, northern harriers, and even cranes and egrets, rails need a complex structural attributes in order to thrive. A monotype of reed canary grass, might be difficult to navigate even for a hardy Virginia rail, and this monotype lacks the diverse structure that allows for great feeding opportunities.
For instance, at the Laas Tamarack—where rails have been discovered breeding—a view from above shows the complex habitat that rails enjoy.
The Laas Tamarack is one of Faville Grove’s delightfully diverse habitats. Map created by Drew Harry
I’ve been through this area on foot, and it contains open water, floating mud flats, floating areas with dense cattails, elevated mounds of tussock sedges, elevated mounds from muskrat lodges, wet pockets of sedges and blue flag iris, hummocky areas of sphagnum moss, and willows, bog birch, and red osier dogwood. This diversity of habitat provides good cover and foraging and nesting spots for a rail.
Blue flag iris, within the wetland complex at the Laas Tamarack. Photo by Drew Harry
In addition, where the mean C-value is higher (which corresponds to high-quality vegetation), there tend to be more Virginia rails.
At Faville Grove, we strive to reduce the reed canary grass as much as possible, and our restoration plantings focus on biodiversity and often result in high mean C values. All of this makes good habitat for rails, and last year a Breeding Bird Atlas volunteer found an adult Virginia rail with its young in the sanctuary.
You might hear Virginia rails around dawn or dusk in any of the marshy spots around the sanctuary, but with high water levels, it’s even more difficult than usual to navigate these spots. Living up to its reputation as a secretive marsh bird, a Virginia rail sighting may remain elusive this year.